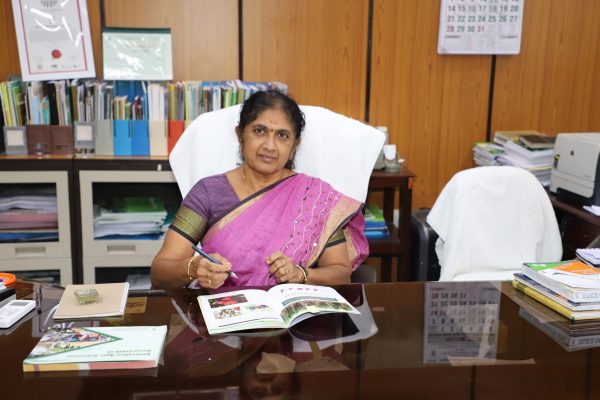
From the Director's Desk

ICAR-Sugarcane Breeding Institute celebrated its 111th Foundation day on 18-11-2022 and the long journey of the Institute has been wonderful, studded with an array of improved sugarcane varieties released in intervals to transform our Mother India into a sugar surplus country and as an exporter of sugar in the recent years. The total sugar production is expected to be a record figure of 38 MT in 2022, and achieving 10 per cent blending with petrol in 2022 would be a reality, a target fixed for 2025. The average sugarcane production of the country (81.98 t/ha) has also surpassed the world average sugarcane productivity of 77 t/ha. This spectacular achievement was mainly possible through its varieties which occupy about 80% area under sugarcane in the country, while over 98% of the area is occupied by the Co and Co allied varieties developed with the support of ICAR-SBI.
The Institute’s variety Co 0238, acclaimed as a wonder variety with extraordinary performance, continued its magical performance benefitting the farmers and millers and dominated subtropical India to cover about 22 lakh ha in 2021 in spite of red rot occurrence and identification of a new virulent pathotype CF 13 from it. The Institute released new varieties such as Co 13013 for Peninsular zone and Co 15023 and Co 14036 for North Western zone. Co 15023, an early maturing sugar rich variety is proving as a suitable complement to Co 0238 especially when planted in spring and summer months. Co 14012 was identified for release in Peninsular zone, which is an improved version of Co 86032, the ruling tropical cane, with increased sugar content and red rot resistance; Co 11015, released for Tamil Nadu has spread to 25000 acres and has proved to be a short duration/ early maturing variety with increased cane yield of 3-11 t/acre and sugar recovery of 0.4 to 1.5 units in different regions in Tamil Nadu. Waterlogging, an unusual phenomenon in sugarcane tracks in UP and adjoining places has been the serious bottleneck to cultivation of sugarcane, which necessitates the need of developing waterlogging tolerant varieties for the region and new varietal testing have been implemented in 2021.
Breeding superior varieties initiatives with increased resilience to climate change is a main focus of Crop Improvement Division and is taken up in a multidisciplinary mode. This year, seven genetic stocks possessing drought and water logging tolerance, ratooning ability, high biomass were registered with ICAR-NBPGR. Hitherto unutilized basic species clones for different traits are incorporated in the pre-breeding programme. In order to support pre-breeding program, speed breeding facilities are under establishment. Sugarcane is a short-day plant, hence requires a different approach to induce flowering. Speed breeding protocols are being developed to study the effect on crop growth and flowering. The creation of this new facility would help in the development of new varieties and faster advancement of backcross generations in introgression breeding, production of inbred lines for genetic studies, transfer of GM events from a single cultivar into a range of backgrounds, in true seed production and population development through recurrent selection.
True seed based sugarcane agriculture needs the development of true breeding parental lines and significant progress was made through inbreeding approach aided with molecular genotyping and phenotyping to identify and advance the best performing near homozygous lines. Inter-crossing of sixth generation selfs could produce less segregating hybrid populations with increased hybrid vigour was demonstrated for the first time in sugarcane. More focused efforts are in progress. Under the fluff supply programme, participating centers were facilitated to make crosses in the National Hybridization Garden and National Distant Hybridization Facility at ICAR-SBI RC, Agali. In order to develop genetic stocks for different stresses specific to the sugarcane growing tracks of India, a minimum of five wide crosses were made for each participating center. Constant demand of good quality sugarcane seed has been largely met with farmers’ participatory seed production.
During 2014-21 period, 7305 tonnes of quality breeder seed from Coimbatore and 8764.6 tonnes from Karnal were produced and supplied and has resulted in the substitution of old and degenerated seed and in controlling seed borne diseases, while ensuring realization of increased yield. Keeping in view of the occurrence of diseases, the institute has developed a Sett Treatment Device for disease management and healthy nursery programme in sugarcane and with its success, an inter-institutional project has been initiated to validate the device in other vegetatively propagated crops viz., banana (ICAR-NRCB), tuber crops (ICAR -CTCRI), tapioca (TNAU), ginger and turmeric (ICAR-IISR, Calicut) and ornamental crops (ICAR-IIHR).
With the goal of establishing gene editing in sugarcane, more candidate genes such as Phytoene Desaturase (PDS) gene and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G (elF4G) were targeted to validate the genome editing through CRISPR/Cas9 mediated gene editing. Novel miRNAs were identified for drought and salinity tolerance. Through comparative transcriptome sequencing and analysis differentially expressing drought responsive genes viz., Expansion (EXPA1) and Glyoxalase (Gly III), Nuclear Factor Y (NFYB2) and Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) were structurally and functionally validated and transgenic events were developed. A part of the transgenic events was multiplied after confirming increased drought tolerance and promising events for further screening under confined field conditions were identified. Insulin and Interferon (Ifn2A) gene constructs for vacuole targeting are also being used to develop for value addition. Genomic selection in sugarcane progressed and the prediction methods Bayes models and RKHS Single and RKHS- averaging were promising.
As the field trials with Bt-62 caused 60% reduction in white grub population, whole genome sequencing of Bt 62 genome and further studies revealed the presence of two cry genes viz., cry8Sa1 and cry8Ib of which Cry8Sa1 toxin caused significantly higher mortality up to to 95%. A Sugarcane Based Farming system demonstration unit was inaugurated at the Institute by the Director General ICAR and Secretary, DARE Dr. Trilochan Mohapatra on 1-11-2021. This system consists of the components such as goat, dairy, poultry, fish culture, vermicompost, sugarcane settling production, and mushroom production, for demonstrating to small sugarcane farmers to double their income. Weed management using early post emergence application generation herbicide molecules, intercropping, water and radiation use efficiency in commercial and selected species clones were focused.
Light interception under different spacings and basal temperature for flowering in different varieties, Soil Inference System (SIS) Software with soil constraint identification and management measures and technology integration for maximizing productivity and profitability also gave encouraging results. More number of new implements were developed in collaboration with the Central Agricultural Engineering Institute, Coimbatore station. A modified version of IISR Lucknow’s tractor operated two row sugarcane sett cutter planter was developed as a technology with an efficiency of saving 54% cost of planting operation when compared to conventional planting.
Red rot management remained the major focus and 1524 resistant genotypes were identified from the breeding materials. Critical analysis of the role of sugarcane microRNAs and their target genes during sugarcane – C. falcatum interaction provided new insight into the miRNA mediated defence mechanism in sugarcane. Nano formulation application under field conditions could reduce fungal diseases significantly in susceptible varieties. Proteomics studies identi fied 13 proteins representing the smut pathogen. Pokkah boeng disease led to crop losses in Tamil Nadu along with mealy bug if spindle region is infested. Virus indexing service continued to index tissue culture raised plants from different tissue culture production labs. The field-release station standardized for the larval parasitoid Cotesia flavipes has been tested for egress of the egg parasitoid Telenomus dignus. Two novel cry1 genes viz cry1D and cry1E were cloned in acrystalliferous Bt isolate SBI-KK 27. Bioassay indicated that Cry1D showed 90% growth and developmental retardation in pink boll worm resistant to Bollgaurd II cotton.
In field trial with EPFs Metarrhizium anisopliae + Beauveria brongniartii against white grub also showed significant reduction of white grub. Three novel ICAR-SBI EPN formulations containing Heterorhabditis bacteriophora strain SBILN8, Steinernema siamkayai strain SBITNT1 and Steinernema surkhetense strain SBIP3 were developed with longer shelf life of 10-12 months with viable infective nematode juveniles. Heterorhabditis indica strain SBITNAUHI3 was found to be more virulent against fall Army worm causing 50% mortality of the 2nd instar larvae. The institute made a big head way in the commercialization of technologies like EPN, soil moisture indicator, settling planter, Sett Treatment Device, sugarcane settling mechanical planter, tractor operated two row sugarcane sett cutter planter, sugarcane jam, liquid jaggery and bio-control agents against white grub.
The ICAR-SBI EPN Biopesticide formulation technology has been commercialized to five firms with the co-ordination of AGRINNOVATE INDIA, New Delhi. The AgriBusiness Incubator of the Institute, named as ‘SugarcaneEdge’ is fully operational. The incubatees for cane jam and liquid jaggery production were given training and handholding. Karnal and Kannur centres made a big progress in developing new products from sugarcane and their marketing. Significant improvement in publication of articles in high NAAS rated journals, winning the prestigious “National Water award” by the team of scientists who developed SMI and, several awards and fellowships from various reputed scientific societies brought laurels to the Institute. The institute HRD activity covered all the categories of staff during the past five years. The Institute has successfully implemented Central Government flagship programmes including Mera Gaon Mera Gaurav, Swachchh Bharat Abhiyan, SPC, SCSP, Soil Health Cards etc.
Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav programme was launched at the institute from 16-7-2021 coinciding with the Foundation day of ICAR. Different activities including lectures, campaigns, contests and displays were organised at the main institute and its regional/ research centres. It is ensured that at least a function was organized every week. Eminent scientists from different streams of science, agriculture and medicine delivered talks useful to all employees, in addition to campaigns, competitions and events organized for the benefit of staff, students, children, women, farmers, and economically weaker sections of the society.
The year 2022 was an eventful year of many research achievements and with greater participation of staff members in various events. I wholeheartedly thank all scientists and other staff of the Institute towards this achievement. This Annual Report is presented encompassing the research summaries and other activities of the Institute. I thank the editorial board for their dedicated efforts to beautifully bring out this publication. I gratefully acknowledge the constant encouragements and support provided by Dr. T. Mohapatra, Secretary DARE and DG,ICAR, Dr. T.R. Sharma, DDG (CS) ICAR, Dr. R.K. Singh, ADG (CC) ICAR and Dr Bakshi Ram,who was the Director of the institute till June,2021.
Contact Address
-
ICAR-Sugarcane Breeding Institute
Veerakeralam,
Coimbatore 641007
Tamil Nadu. - Phone: 0422 - 2472621
- Email: director.sbi@icar.gov.in
- GST Number 33AAAAD2962K2ZT
Our Visitor Count